Technologies driving traceability

The impact of technology on our lives is all pervasive. And when it comes to complexities of managing and tracing a supply chain, technology has revolutionized how it is done over the last couple of decades. Even in the early 2000s, tracing the origin and journey of products or information was a time-consuming and complex process that required logging every record painstakingly into a ledger, filing every invoice and purchase order, and tracking movement of goods via a paper trail.
Although supply chain traceability is a requirement in every industry today, the stakes are higher in the food and beverage sector where food safety and ingredient tracing are of paramount importance. And the growth of possibilities within a traceable supply chain has been driven by advancements in technology.
So, what are the technologies that have transformed the way traceability works and are likely to shape the future?
Barcodes to QR Codes
Barcodes are among the first of the technologies used in inventory tracking, and store limited information, such as serial number, price, and so on. Though barcodes are still commonplace, QR codes also known as quick response codes, are more widely used in supply chain management as they hold a vast amount of information about the product, such as sourcing, ingredient list, and can be scanned using just a mobile phone.
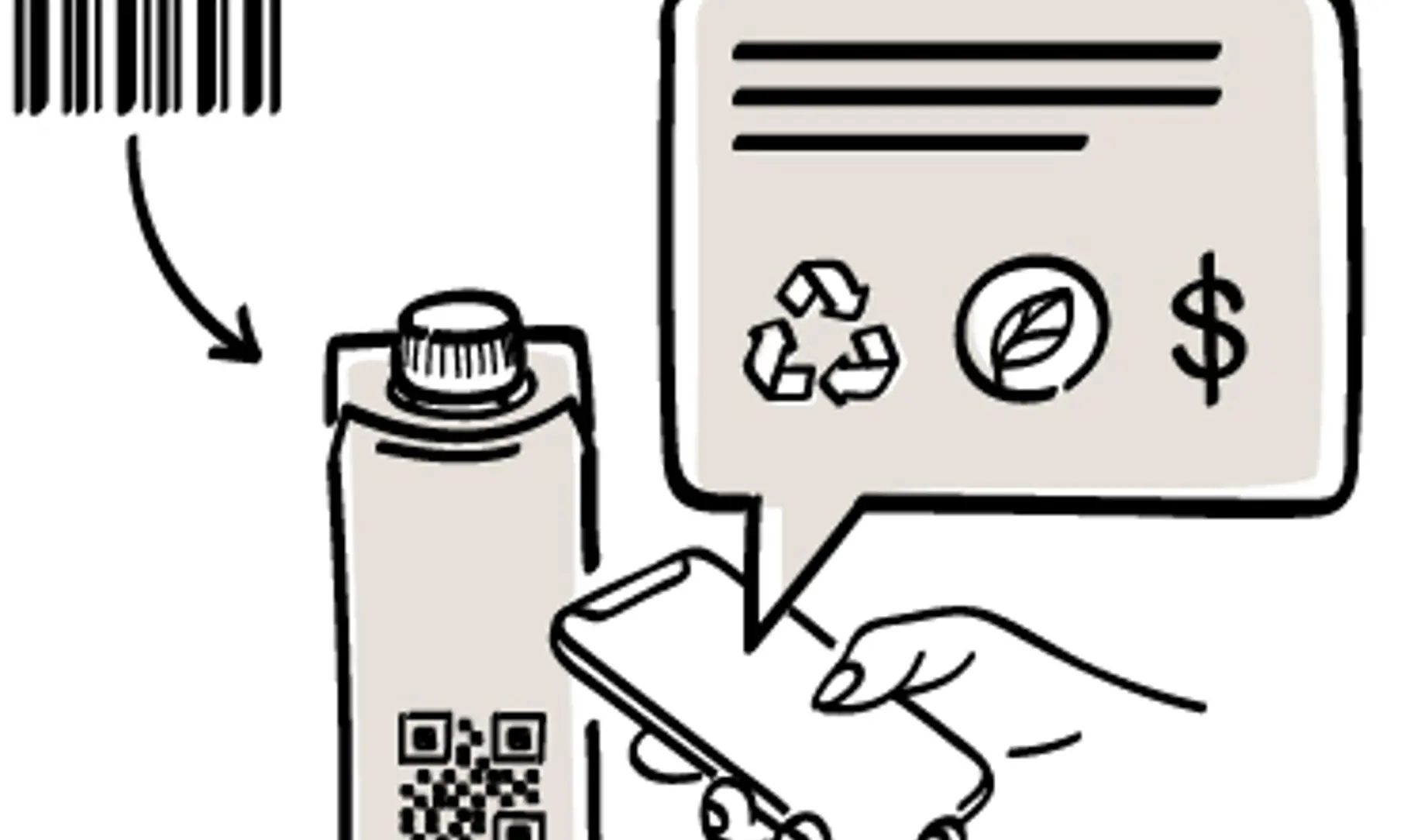
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
RFID technology uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify, and track the tags attached to objects. RFID tags can be attached to individual products or pallets, enabling real-time tracking of various aspects across multiple points in the supply chain, including temperature monitoring and storage conditions. The ease of scanning RFID tags makes it a popular, low-maintenance technology. Hundreds of tagged items can be scanned simultaneously by a single scanner located within a specific radius.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT enables refers to a network of interconnected physical devices that can share information with each other. This data is instrumental in establishing traceability across the supply chain. The potential of IoT is vast and can include everything from monitoring environmental conditions at sourcing to tracking consumption. IoT is driven by a combination of technologies such as sensors, cloud computing, big data, and more.
Blockchain
Blockchain, which was once known for only cryptocurrency and finance, is today a top enabler of a traceable supply chain. A secure, permanent ledger of transactions, blockchain records every transaction related to a product in a block and links it together. Each block contains the timestamp of the transaction and stakeholders, creating a trail of every step of the product’s lifecycle. The recorded data is tamper-proof and fosters trust and transparency across the value chain.
End to end traceability continues to be a rapidly developing area and it is only a matter of time before newer, innovative technologies take supply chain management to the next level. For now, some of the other technologies that are key in a traceable supply chain include: cloud-based platforms for real-time access and collaboration; mobile applications for anytime anywhere access; geospatial technology, and artificial intelligence, among others. Also, dedicated track and trace systems, such as PAC.TRUST, integrate various technologies to help manufacturers get all the benefits in one system.
In the next part of the series, we will delve into the benefits of a traceable value chain for manufacturers. Subscribe to our exclusive bi-weekly newsletter and get it straight in your inbox.
- august 31, 2023
